Why Is RFID Technology An Advancement Over Barcodes?
Introduction
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has revolutionized the way businesses track and manage their inventory, assets, and products. It is a powerful tool that offers numerous advantages over traditional barcode systems. In this article, we will explore why RFID technology is considered an advancement over barcodes.
Barcodes have been a staple in the retail industry for decades, allowing businesses to quickly and accurately scan product information at the point of sale. However, barcodes have limitations when it comes to tracking individual items throughout the supply chain or in large inventory management scenarios. This is where RFID technology comes in.
RFID technology uses radio waves to transfer data between a reader and an RFID tag. Each tag contains a unique identifier, similar to a barcode, but with the added ability to store and transmit additional information. This makes RFID technology more versatile and efficient compared to barcodes.
RFID technology is now being widely adopted across various industries due to its many advantages. In the following sections, we will discuss the key differences between RFID and barcodes, the advantages of RFID technology, its use cases and applications, as well as the challenges and limitations associated with its implementation.
What are RFID and Barcodes?
Before we delve into the differences and advantages of RFID technology, let’s first understand what RFID and barcodes are.
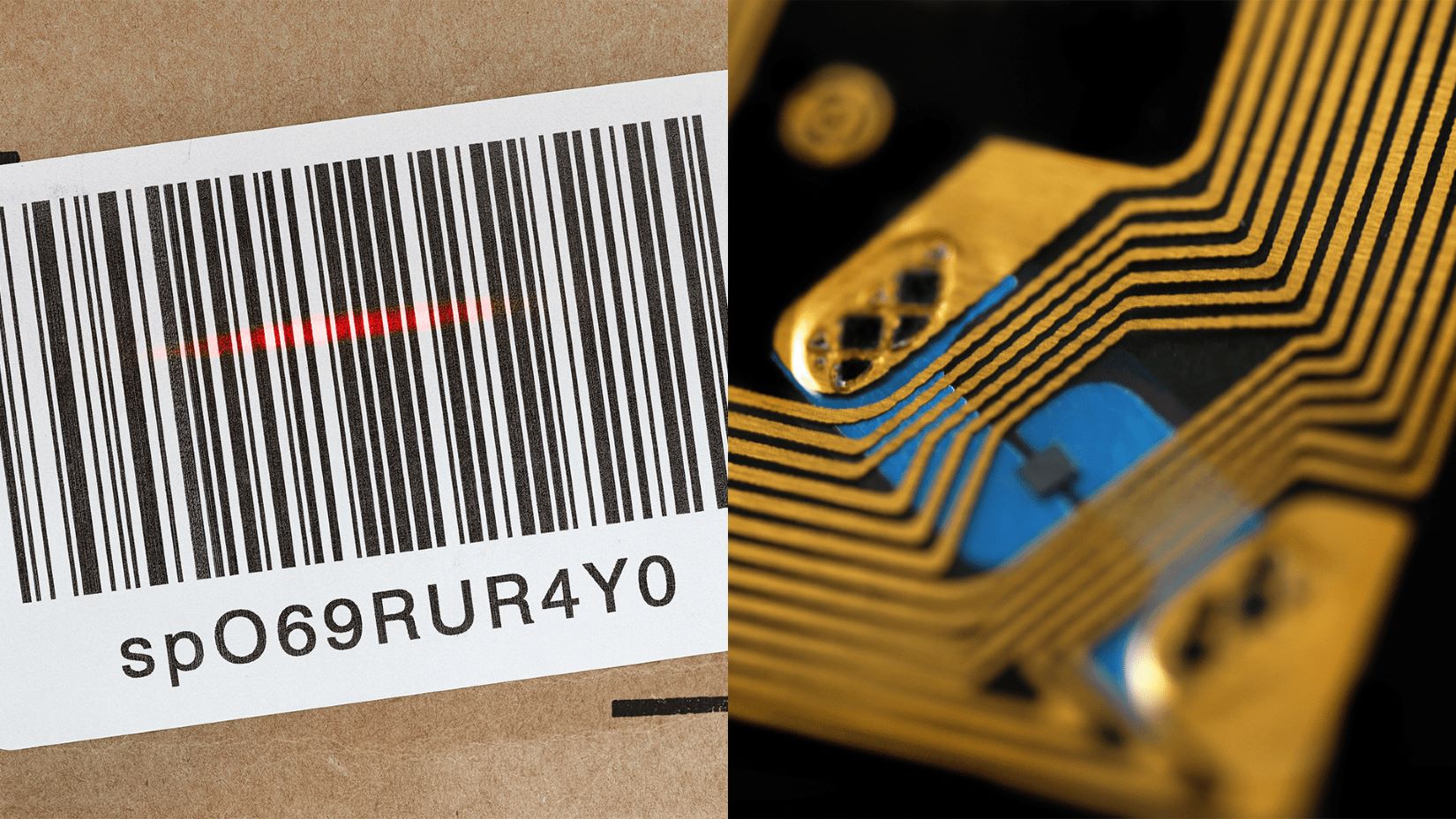
Barcodes are a familiar sight in the retail industry. They consist of a series of black bars and white spaces of varying widths, which represent different numbers or symbols. These codes are scanned by a barcode reader to retrieve product information, such as the name, price, and stock level.
RFID, on the other hand, stands for Radio Frequency Identification. It utilizes radio waves to transfer data between an RFID reader and an RFID tag. An RFID tag is a small electronic device that is attached to an object, whether it’s a product, asset, or inventory item. It contains a unique identifier as well as additional data that can be stored and transmitted.
Unlike barcodes, which require direct line-of-sight scanning, RFID tags can be read remotely and do not require a clear line of sight. This means that items with RFID tags can be read even if they are inside containers or packages. Additionally, RFID tags can be read more quickly and in bulk, making them highly efficient for inventory management and tracking purposes.
Rather than relying on a simple numeric or alphanumeric code, RFID tags can store larger amounts of data, including information about the item’s origin, manufacturing date, and individual characteristics. This added flexibility and capacity make RFID technology a superior choice for industries that require more comprehensive tracking and information management capabilities.
RFID technology also allows for both read and write capabilities, meaning that the data on the RFID tag can be modified or updated as needed. This enables businesses to have real-time access to accurate and up-to-date information about their products or assets.
In the next sections, we will explore the key differences between RFID and barcodes and why RFID technology offers significant advantages over traditional barcode systems.
Key Differences Between RFID and Barcodes
RFID technology offers several key differences compared to traditional barcodes. Let’s explore the main differentiating factors:
- Data Storage: Barcodes can store a limited amount of data, usually up to 20 characters, while RFID tags can store much more information, ranging from a few kilobytes to several megabytes. This allows for more detailed and comprehensive data to be associated with each item.
- Scanning Method: Barcodes require direct visual scanning using a barcode reader, with the barcode and scanner needing to be in close proximity. RFID tags, on the other hand, can be remotely scanned using radio frequency waves, allowing for a quicker and more efficient scanning process.
- Scanning Speed: Barcode scanning is typically a manual process that requires line-of-sight scanning, which can be time-consuming when dealing with large quantities of items. RFID technology enables simultaneous and bulk scanning, with the ability to read multiple tags at once, resulting in faster and more accurate data collection.
- Environmental Factors: Barcodes can be easily damaged or rendered unreadable by wear and tear, as well as exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture, or harsh chemicals. RFID tags are more durable and resistant to environmental factors, allowing for reliable tracking and identification even in challenging conditions.
- Reusability: Barcodes are typically one-time-use and cannot be easily modified or updated. RFID tags are reusable and can be rewritten or updated, allowing for dynamic and real-time data management.
- Distance: Barcodes require close proximity for scanning, while RFID tags can be read from a distance, even through non-metallic materials. This makes RFID technology ideal for scenarios where items need to be identified or tracked without direct access.
These key differences highlight the superior capabilities of RFID technology compared to traditional barcodes. The ability to store more data, scan quickly and remotely, withstand harsh environments, and enable dynamic data management makes RFID a valuable asset in various industries.
Advantages of RFID Technology
The adoption of RFID technology offers numerous advantages over traditional barcode systems. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
- Efficiency: RFID technology allows for faster and more accurate data collection. With the ability to read multiple tags simultaneously and from a distance, businesses can quickly and efficiently track and manage their inventory, assets, and products.
- Real-time Tracking: Unlike barcodes, which require manual scanning, RFID technology enables real-time tracking and monitoring of items. This provides businesses with up-to-date visibility into their supply chain, allowing them to make informed decisions and respond quickly to changes or issues.
- Automation: RFID technology can be integrated into automated systems, enabling seamless and efficient workflows. This eliminates the need for manual data entry or scanning, saving time and reducing human error.
- Increased Data Capacity: RFID tags can store more comprehensive and detailed information, allowing businesses to track and manage additional attributes associated with each item. This data can include expiration dates, batch numbers, maintenance history, and more.
- Enhanced Security: RFID technology offers enhanced security features, such as encryption and password protection, to prevent unauthorized access or tampering of data. This helps businesses protect sensitive information and maintain the integrity of their tracking systems.
- Improved Inventory Management: With RFID technology, businesses can efficiently monitor and manage their inventory in real-time. This enables accurate stock counts, reduces stockouts, minimizes overstock situations, and improves overall inventory accuracy.
- Reduced Loss and Theft: RFID tags can be discreetly placed inside items, making them difficult to remove or tamper with without detection. This helps reduce the risk of loss or theft and provides businesses with better control over their valuable assets.
These advantages highlight the significant value that RFID technology brings to various industries, including retail, logistics, manufacturing, healthcare, and more. By leveraging the capabilities of RFID, businesses can optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and drive overall growth and success.
Use Cases and Applications of RFID Technology
RFID technology has found applications across a wide range of industries, proving its versatility and effectiveness in various use cases. Let’s explore some of the key applications of RFID technology:
- Inventory Management: RFID technology is widely used for inventory management in industries such as retail, manufacturing, and logistics. It enables automated tracking of stock levels, real-time monitoring of item locations, and efficient management of supply chains.
- Asset Tracking: RFID tags can be attached to assets such as equipment, vehicles, or tools, enabling businesses to track their location, usage, and maintenance history. This helps prevent loss, optimize asset allocation, and streamline maintenance processes.
- Supply Chain Optimization: RFID technology enables end-to-end visibility and traceability in the supply chain. It facilitates efficient inventory management, accurate order fulfillment, and timely delivery, resulting in cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
- Authentication and Security: RFID tags can be used for authentication and security purposes, such as access control to restricted areas, identification of authorized personnel, and protection against counterfeiting and theft.
- Smart Retail: RFID technology enables retailers to improve the shopping experience by implementing smart fitting rooms, automated checkout systems, and real-time inventory availability tracking. This enhances customer satisfaction, reduces shrinkage, and streamlines retail operations.
- Healthcare: RFID technology offers significant benefits in healthcare settings, facilitating patient tracking, asset management, medication tracking, and equipment sterilization monitoring. This helps streamline processes, improve patient safety, and enhance operational efficiency.
- Livestock and Agriculture: RFID tags are used for tracking and managing livestock, enabling farmers to monitor animal health, track breeding records, and ensure traceability in the food supply chain. In agriculture, RFID technology is used for inventory management, crop monitoring, and pest control.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of RFID technology in different industries. The versatility and functionality of RFID technology make it a valuable tool for businesses looking to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and enhance overall productivity.
Challenges and Limitations of RFID Technology
While RFID technology offers numerous advantages, it is important to be aware of the challenges and limitations that businesses may encounter when implementing RFID systems. Let’s explore some of these challenges:
- Cost: Implementing RFID technology can involve significant upfront costs, including the purchase of RFID equipment, tags, and software integration. However, as the technology continues to advance, costs are gradually decreasing.
- Read Range: The read range of RFID tags can vary based on factors such as tag type, frequency, and environmental conditions. In some cases, the read range may be limited, requiring businesses to strategically position readers to ensure reliable tag detection.
- Interference: RFID signals can be subject to interference from other devices or materials, such as metals or liquids. Businesses need to carefully consider the surrounding environment and select appropriate RFID frequencies to minimize interference issues.
- Data Privacy and Security: RFID technology raises concerns about data privacy and security. Without proper encryption and data protection measures, unauthorized individuals may be able to intercept or tamper with RFID signals, compromising sensitive information.
- Standardization: The lack of global RFID standards can lead to compatibility issues and hinder interoperability between different systems and vendors. However, efforts are being made to develop and promote standardized RFID solutions.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating RFID technology into existing business systems and processes can be complex and require significant planning and coordination. It may involve modifications to infrastructure, software configurations, and employee training.
- Environmental Factors: RFID performance can be affected by environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, or physical obstructions. Businesses need to carefully assess their operating environment and select suitable RFID tags and readers accordingly.
Despite these challenges, advancements in RFID technology are constantly being made, addressing many of the limitations and enhancing its functionality. It is crucial for businesses to conduct thorough research, work with reputable vendors, and carefully plan their RFID implementation strategy to overcome these challenges and fully leverage the benefits of this technology.
Conclusion
RFID technology has undoubtedly emerged as a game-changer in various industries, offering significant advantages over traditional barcodes. Its ability to store larger amounts of data, remotely and quickly scan items, withstand harsh environments, and enable real-time tracking and management has revolutionized inventory management, asset tracking, and supply chain optimization.
RFID technology has found applications in diverse areas, including retail, healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, and agriculture. It has enhanced efficiency, improved inventory accuracy, reduced loss and theft, and streamlined processes, leading to increased productivity and customer satisfaction.
While there are challenges and limitations associated with RFID implementation, such as cost, read range, and data security, the continuous advancements in RFID technology are addressing these issues and making it a more accessible and reliable solution for businesses.
In conclusion, RFID technology is expanding opportunities for businesses to optimize their operations, improve inventory management, enhance security, and deliver superior customer experiences. By embracing RFID technology and carefully considering its implementation, businesses can unlock new levels of efficiency, accuracy, and competitiveness in today’s dynamic and demanding market.

